The chemical giant, world leader in the printing ink sector (and not only), publishes its year-end environmental balance. Focus on actions aimed at reducing global CO2 emissions and increasing the use of renewable and recyclables; but aboveall their new product formulas, increasingly greener.
The more important you are, the greater the environmental consequences of your work and therefore also your responsibility: an obvious statement, but seeing what it means in practice is always somewhat striking.
Sun Chemical, a member of the DIC group, is a world leader in the production of inks, varnishes and additives, pigments, polymers, liquid and solid compounds and printing materials, as well as of adhesives for laminating film, paper and aluminum, with an annual turnover of over 7.5 billion dollars and more than 20,000 employees spread over 176 locations in 63 countries. At the beginning of the year it published its environmental and social responsibility balance which shows, through the results obtained, how the chemical giant, which in Italy works with a direct branch, two factories and research centers that are benchmark for the entire group, interprets this responsibility.
From bright ideas to global warming …
The first chapter of each Sustainability Report concerns the use of resources and in particular the reduction of raw material consumption (starting from energy) and pollution. Sun Chemical has set itself high objectives and the results are in proportion, thus showing at the same time what the margins of intervention are in this field.
On the energy front, for example, Sun Chemical had stated that it wanted to cut consumption by 5% in the 2016-18 three-year period, but in reality it has achieved much higher savings (by 6.3%) and showed on how many levels one can intervene. A nice example of a “bright idea” in this regard was offered by one of the Italian sites where, “simply” replacing the traditional metal halide and mercury vapor lamps with LED devices, they halved the energy needed to illuminate the site, with a saving of 350 MWh/year.
But it is in the subject of CO2 emissions that Sun Chemical has set the most ambitious targets, envisaging a reduction of emissions of at least 30% and stating that if the whole industry adopted these parameters climate change could be controled and global warming reduced a mere + 2 ° C.
… going by way of CSR
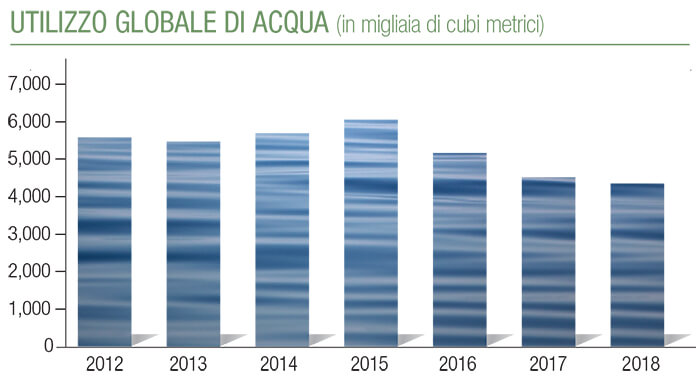
In Sun Chemical, the responsible exploitation of resources also concerns water (used in large quantities to produce pigments), the consumption of which fell by 32% between 2016 and 2018, the increasingly efficient and less polluting management of waste , and heads in the direction of Corporate Social Responsibility, which also includes the human environment in the “environment” to be safeguarded.
On this level, Sun Chemical documents accident rates that are significantly below the industrial average, following the intense work carried out to improve worker safety, as well as the constant monitoring of supply chains, with particular attention to combating the phenomena of exploitation of child labor.
Water-based inks and barrier coatings: The new frontier
But the most visible progress regards the goals achieved by product R&D, stimulated by the urgent requests of the brand owners – and we all know how much pressure the green promises made to consumers by the food majors generate on packaging suppliers. Here the developments concern three main areas: raw materials, functionality and end of life.
Working on raw materials, Sun Chemical is now able to offer many inks with a high level of renewable content. AquaGreen Sun Chemical water-based flexographic inks are an important example of a renewable bio product and are used, to cite an exemplary case, to print McDonald’s packaging.
The chapter on the functional aspects of Sun Chemical products, which help to preserve the durability and quality of its content – especially if it is food – also saw very significant goals. Two examples for all: the development of adhesives and paints with a gas barrier effect and the innovative UV light barrier varnishes that allow the passage of visible light and thus allow the adoption of transparent windows in the packaging of products sensitive to UV rays.
Recyclability and food contact
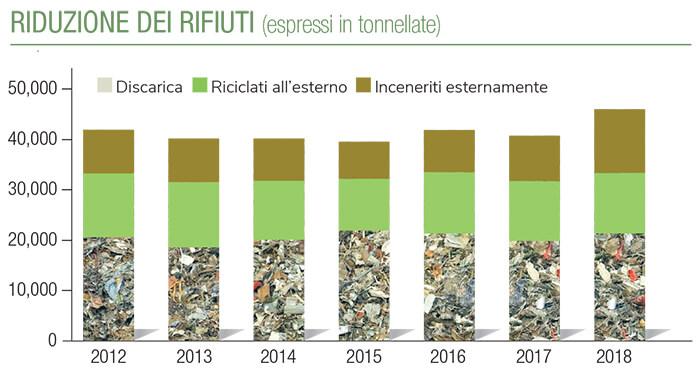
The end-of-life chapter, complex and varied, deals with the recycling and the development of circular economies. Here the paths are truly many and we limit ourselves to citing some examples both of the complexity of the matter and of the results achieved by the multinational’s R&D work.
Our thoughts go to the new varnishes for the interior of paper cups, alternatives to the traditional layer of PE all to the advantage of their recyclability. Paper cups treated with Sun Chemical’s “repulping” varnish can be disposed of together with standard cardboard waste and easily recycled paper fibers. Our thoughts also go to Sun Chemical’s ever-growing portfolio of certified compostable inks, but also to the innovative de-inking technology based on the SunLam™ anti-caking adhesive, which allows you to remove or separate the ink from the printed packaging, facilitating the recovery of the secondary raw material.
Lastly, a further mention of the inks compatible with direct food contact, also applied to color paper straws used as an alternative to plastic straws, and to the new generation of pigments that comply with the rules on the heavy metal content (that need to be reduced).